


How to restrict SSH access only to specific IPs 17323 25.How to configure a static IP on Linux 17692 9.11 Ways to free up disk space on cPanel servers 18365 11.Install packages in Arch Linux from AUR 20003 17.centos GitLab RHEL Scientific Linux Installations That’s it! You now have a functioning git service running on your own cloud instance. It’s recommended to change the username of the default account from root to something else. You should be able to log in with the password you set before. Enter a desired password and click ‘Change your password’.Īfter you change the password, you will be taken to the login page. You will be redirected to a page where you’ll be asked to enter a new password. To do this, simply navigate to the hostname or the IP address of your instance from your web browser. You just need to visit it from your browser and change your password. Your GitLab installation is now almost complete. Configure and Start GitLabĪfter the installation is complete, we need to configure GitLab.
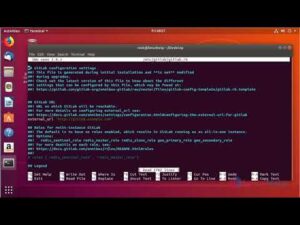
Type y at the prompt and press Enter to continue. Sudo systemctl reload firewalld Install GitLabįirst, add the GitLab package server. Sudo firewall-cmd -permanent -add-service=http sudo yum install curl policycoreutils openssh-server openssh-clients On CentOS, you might also need to open HTTP access in the system firewall.Įnter the following commands one by one to install and configure the dependencies and configure the firewall. You will need to install curl policycoreutils, openssh and a mail server. sudo yum update Install and Configure the Dependencies Make sure your instance meets the recommended requirements for GitLab. It includes Git repository management, issue tracking, code review, an IDE, activity streams, wikis, built-in Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment and much more features. GitLab Community Edition is an open source git service which you can easily deploy in your cloud server.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
